Cloud Computing
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and more—over the Internet (the cloud) to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale. Instead of owning physical hardware or managing on-site data centers, businesses can access computing resources on-demand from cloud service providers.
Key Characteristics of Cloud Computing:
On-Demand Self-Service: Users can provision computing resources as needed, without requiring human intervention from the service provider.
Broad Network Access: Cloud services are accessible over the internet from various devices such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets.
Resource Pooling: Cloud providers serve multiple customers using a multi-tenant model, sharing resources to achieve economies of scale.
Rapid Elasticity: Cloud resources can be scaled up or down quickly to meet changing demand, allowing businesses to optimize costs and performance.
Measured Service: Cloud usage is monitored, controlled, and billed based on consumption, offering transparency and cost control for users.
Types of Cloud Services:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, such as virtual machines, storage, and networking.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without dealing with infrastructure complexities.
Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis, eliminating the need for local installation and maintenance.
Benefits of Cloud Computing:
Cost Efficiency: Businesses can reduce capital expenditure on hardware and infrastructure, paying only for the resources they consume.
Scalability: Cloud services offer the flexibility to scale resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance without over-provisioning.
Agility and Innovation: Rapid deployment of resources and access to cutting-edge technologies enable faster innovation and time-to-market for new products and services.
Reliability and Disaster Recovery: Cloud providers offer redundant systems, backup, and disaster recovery solutions, enhancing data reliability and business continuity.
Global Reach: Cloud services are accessible globally, enabling businesses to reach customers and expand operations across geographical boundaries.
Disadvantages Of Cloud Computing
The following are the main disadvantages of Cloud Computing:
- Security Concerns: Storing of sensitive data on external servers raised more security concerns which is one of the main drawbacks of cloud computing.
- Downtime and Reliability: Even though cloud services are usually dependable, they may also have unexpected interruptions and downtimes. These might be raised because of server problems, Network issues or maintenance disruptions in Cloud providers which negative effect on business operations, creating issues for users accessing their apps.
- Dependency on Internet Connectivity: Cloud computing services heavily rely on Internet connectivity. For accessing the cloud resources the users should have a stable and high-speed internet connection for accessing and using cloud resources. In regions with limited internet connectivity, users may face challenges in accessing their data and applications.
- Cost Management Complexity: The main benefit of cloud services is their pricing model that coming with Pay as you go but it also leads to cost management complexities. On without proper careful monitoring and utilization of resources optimization, Organizations may end up with unexpected costs as per their use scale. Understanding and Controlled usage of cloud services requires ongoing attention.
Impact on Businesses:
Digital Transformation: Cloud computing plays a pivotal role in digital transformation initiatives, enabling businesses to modernize IT infrastructure and processes.
Enhanced Collaboration: Cloud-based tools and platforms facilitate seamless collaboration among remote teams, improving productivity and efficiency.
Data Analytics and Insights: Cloud computing enables businesses to harness big data analytics, gaining valuable insights for informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Scalable E-commerce: Cloud-based e-commerce platforms offer scalability and performance, supporting businesses in handling peak loads during sales events.
Competitive Advantage: Adopting cloud technologies allows businesses to stay agile, competitive, and responsive to market changes, driving growth and innovation.
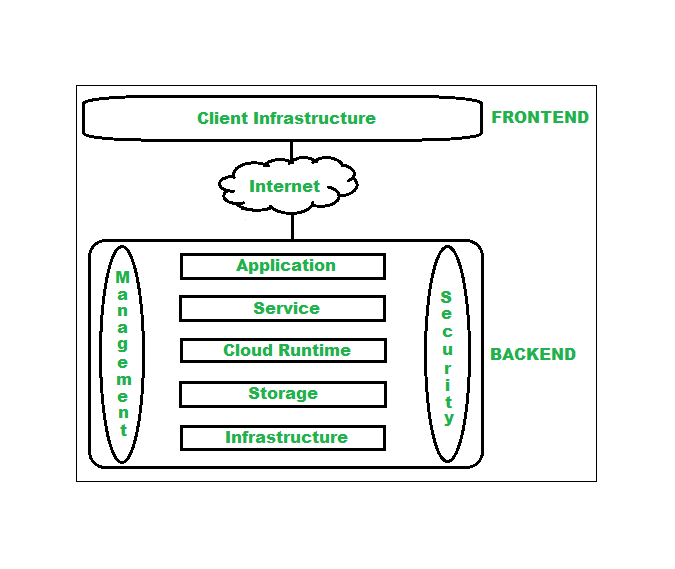
Architecture Of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing architecture refers to the components and sub-components required for cloud computing. These components typically refer to:
- Front end ( Fat client, Thin client)
- Back-end platforms ( Servers, Storage )
- Cloud-based delivery and a network ( Internet, Intranet, Intercloud )
Front End ( User Interaction Enhancement )
The User Interface of Cloud Computing consists of 2 sections of clients. The Thin clients are the ones that use web browsers facilitating portable and lightweight accessibilities and others are known as Fat Clients that use many functionalities for offering a strong user experience.
Back-end Platforms ( Cloud Computing Engine )
The core of cloud computing is made at back-end platforms with several servers for storage and processing computing. Management of Applications logic is managed through servers and effective data handling is provided by storage. The combination of these platforms at the backend offers the processing power, and capacity to manage and store data behind the cloud.
Cloud-Based Delivery and Network
On-demand access to the computer and resources is provided over the Internet, Intranet, and Intercloud. The Internet comes with global accessibility, the Intranet helps in internal communications of the services within the organization and the Intercloud enables interoperability across various cloud services. This dynamic network connectivity ensures an essential component of cloud computing architecture on guaranteeing easy access and data transfer.
Cloud Deployment Models
- Private Deployment Model: It provides an enhancement in protection and customization by cloud resource utilization as per particular specified requirements. It is perfect for companies which looking for security and compliance needs.
- Public Deployment Model: It comes with offering a pay-as-you-go principle for scalability and accessibility of cloud resources for numerous users. it ensures cost-effectiveness by providing enterprise-needed services.
Hybrid Deployment Model
It comes up with a combination of elements of both private and public clouds providing seamless data and application processing in between environments. It offers flexibility in optimizing resources such as sensitive data in private clouds and important scalable applications in the public cloud.
Characteristics of Cloud Computing
- Scalability: With Cloud hosting, it is easy to grow and shrink the number and size of servers based on the need. This is done by either increasing or decreasing the resources in the cloud. This ability to alter plans due to fluctuations in business size and needs is a superb benefit of cloud computing, especially when experiencing a sudden growth in demand.
- Save Money: An advantage of cloud computing is the reduction in hardware costs. Instead of purchasing in-house equipment, hardware needs are left to the vendor. For companies that are growing rapidly, new hardware can be large, expensive, and inconvenient. Cloud computing alleviates these issues because resources can be acquired quickly and easily. Even better, the cost of repairing or replacing equipment is passed to the vendors. Along with purchase costs, off-site hardware cuts internal power costs and saves space. Large data centers can take up precious office space and produce a large amount of heat. Moving to cloud applications or storage can help maximize space and significantly cut energy expenditures.
- Reliability: Rather than being hosted on one single instance of a physical server, hosting is delivered on a virtual partition that draws its resource, such as disk space, from an extensive network of underlying physical servers. If one server goes offline it will have no effect on availability, as the virtual servers will continue to pull resources from the remaining network of servers.
- Physical Security: The underlying physical servers are still housed within data centers and so benefit from the security measures that those facilities implement to prevent people from accessing or disrupting them on-site.
- Outsource Management: When you are managing the business, Someone else manages your computing infrastructure. You do not need to worry about management as well as degradation.



Comments
Post a Comment